Sharp to safe: Gallium technology needles
A nover technology to prevent needle stick injury
Needle stick injuries can be quite terrifying. Normally, the sharp needles used in the medical field are stainless steel as they are easier to produce in large quantities and to dispose of easily. However, when misplaced, these needles may accidentally puncture the skin of unsuspecting individuals, usually healthcare workers and sanitary staff, and may lead to the spread of malicious blood-borne infections like HIV, Hepatitis B, and Hepatitis C.
No method is 100% safe as the needle still remains sharp and may carry viruses that may be contagious. Usually, precautions can be taken by
Scoop method: Scooping the syringe cap and pressing down to lock it
Cutting method: Cutting the needle tip
Burning method: Burning the needle to ashes
Gallium is a liquid metal that is solid when cold and melts at body temperature. This element is usually harmless and non-toxic as per recent research. It stays soft after being removed from the body due to the supercooling phenomenon of gallium. Using this element in the medical field can be quite useful. This tranformative IV can be used in injections and catheters.
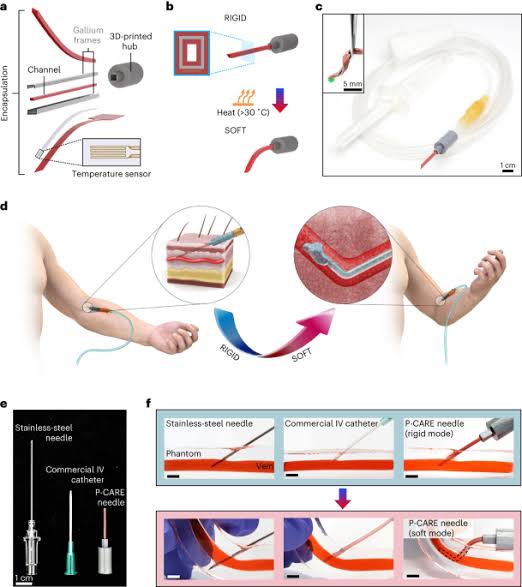
Uses includes
Softens after injection - prevents needle stick injuries
Reduced inflammation
Patient comfort
Prevents needle reuse
Cheaper
Less bleeding
Less vessel damage